reading-notes
Code Fellows reading notes
JavaScript Control Flow, Funtions & Operators
Control Flow
The control flow is the order in which the computer executes statements in a script.
The code is run in order from the first line to the last line,unless the compueter runsa accross the structures that change the control flow, such as conditions and loops.
Meaning, is a script submits validated data, but if the user, say, leaves a required field empty, the script prompts them to fill it in. To do this, the script uses a conditional structure or if…else, so that different code executes depending on whether the form is complete or not.
A typical script in JavaScript includes many control structures, including conditionals, loops and functions. Parts of a script may also be set to execute when events occur.
Functions
A JavaScript Function is a block of codes designed to perform a particular task, which is executed when something calls it.
JavaScript Function Syntax
A JavaScript function is defined with:
functionkey word- followed by a ““name””
- followed by parentheses “”()””
- the code to be executed
Example:

Function invocation
The code inside the function will execute when “something” invokes (calls) the function:
- When an event occurs (when a user clicks a button)
- When it is invoked (called) from JavaScript code
- Automatically (self invoked)
Function Return
When JavaScript reaches a return statement, the function will stop executing.
If the function was invoked from a statement, JavaScript will “return” to execute the code after the invoking statement.
Example:

Why use functions
You can reuse code: Define the code once, and use it many times.
You can use the same code many times with different arguments, to produce different results.
More About JavaScript Functions
Operators

JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
+ |
Addition |
- |
Subtraction |
* |
Multiplication |
** |
Exponenetion |
/ |
Division |
% |
Modulus (Division remainder) |
++ |
Increment |
-- |
Decrement |
JavaScript Assignment Operators
| Operator | Example | Same As |
|---|---|---|
= |
x = y |
x = y |
+= |
x += y |
x = x + y |
-= |
x -= y |
x = x - y |
*= |
x *= y |
x = x * y |
/= |
x /= y |
x = x / y |
%= |
x %= y |
x = x % y |
**= |
x **= y |
`x = x ** y |
Example:

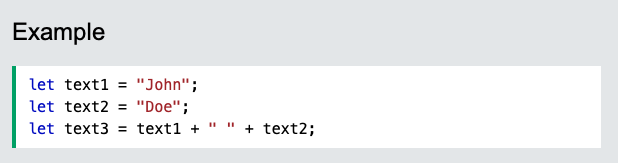
JavaScript String Operators
The + operator can also be used to add (concatenate) strings.